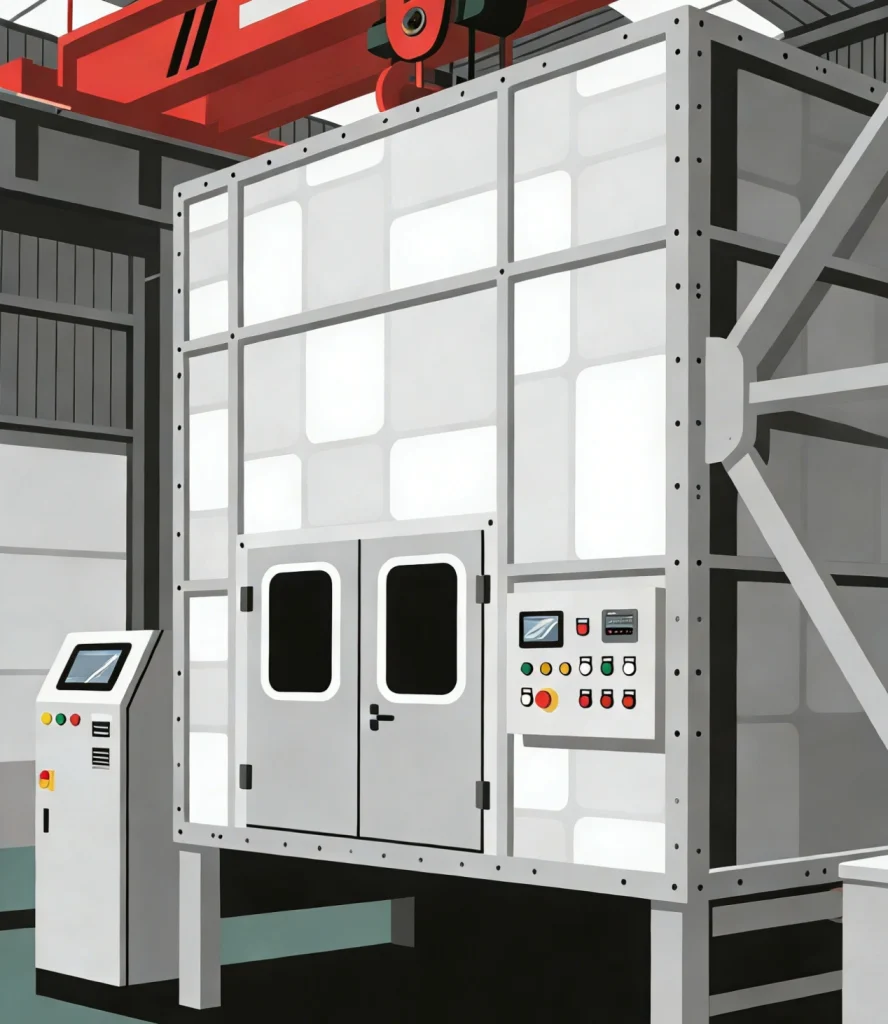
Fire Resistance Test Furnace
Fire Resistance Test Furnace

Our fire resistance test furnaces are engineered to evaluate the fire performance and determine the fire resistance ratings of a comprehensive range of building components and systems. By subjecting specimens to controlled, standardized thermal exposure, they simulate real fire conditions to assess critical capabilities.
Furnace Configurations: Available in vertical, horizontal, and comprehensive layouts with internal dimensions ranging from standard (e.g., 3.0m x 3.0m) to large-scale custom sizes (e.g., 10m x 6m x 2m for curtain walls).
Application Industry:
Building materials manufacturing, fire protection product certification, construction, independent testing and inspection laboratories, research and development institutions, aerospace, rail transportation, petrochemical, power generation, and mission-critical infrastructure.
Test Workpieces / Specimens:
Vertical and horizontal separating elements (e.g., walls, partitions, floors, ceilings), fire doors and windows, fire-resistant glazing, fire shutters and curtains, structural members (beams, columns) with protective coatings, ventilation and smoke extraction ducts, fire dampers, fire-rated fans and dampers, cable management systems (trays, ladders, conduits), building curtain walls, and door sets for smoke control performance.
Applicable Standards:
GB/T 9978 series, GB/T 38252, GB/T 17428, GB/T 26784, GB/T 29415, GB/T 41336, GB/T 41480, XF/T 537, T/CECS 886, GA 211, GA/T 714, and other international (ISO) and industry-specific fire test methodologies, etc.
Available model

Fire Resistance Testing of Building Components
-Comprehensive fire integrity and insulation testing for doors, windows, partitions, and shutters.
-Fire performance evaluation of structural fireproofing, ventilation systems, and building elements including cable trays.
-Additional water spray impact testing capability following standard fire tests.

Fire Door Related Testing
-Overall smoke production characteristic test for fire doors.
-Smoke containment performance testing for fire doors.

Water Spray Impact Testing Machine
-An additional water spray impact test that can be performed when conducting fire resistance tests on building separating elements.
.
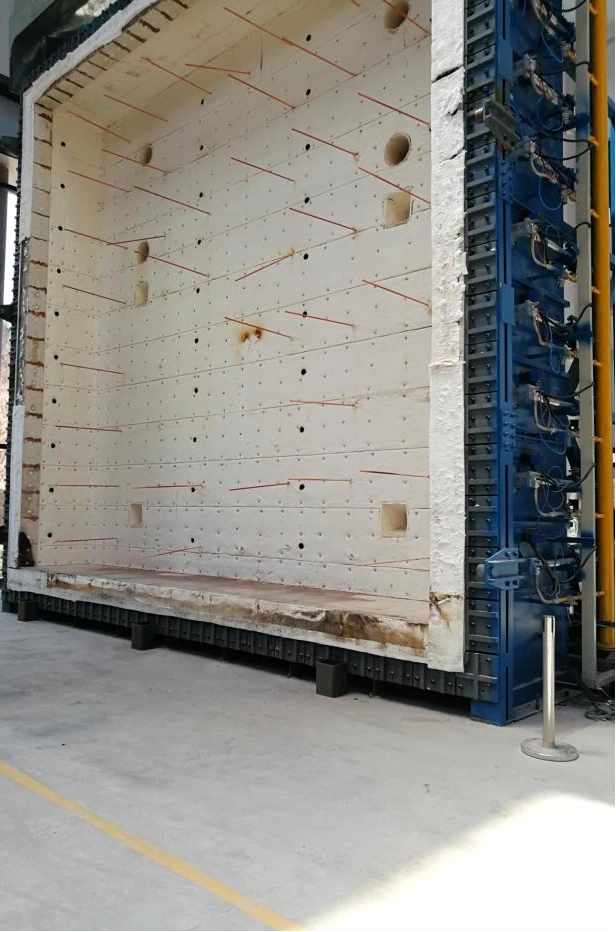
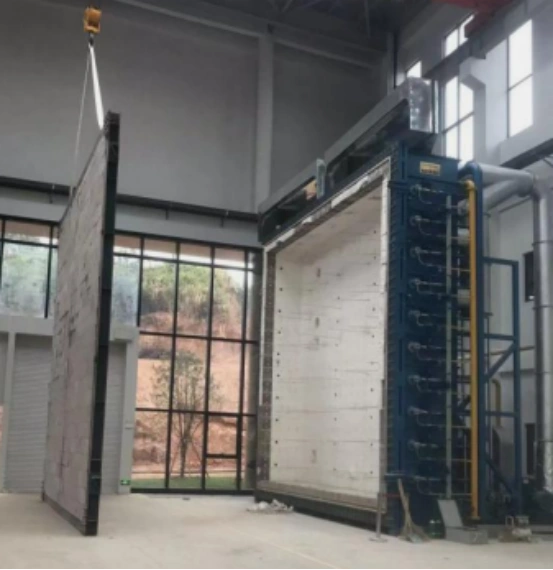




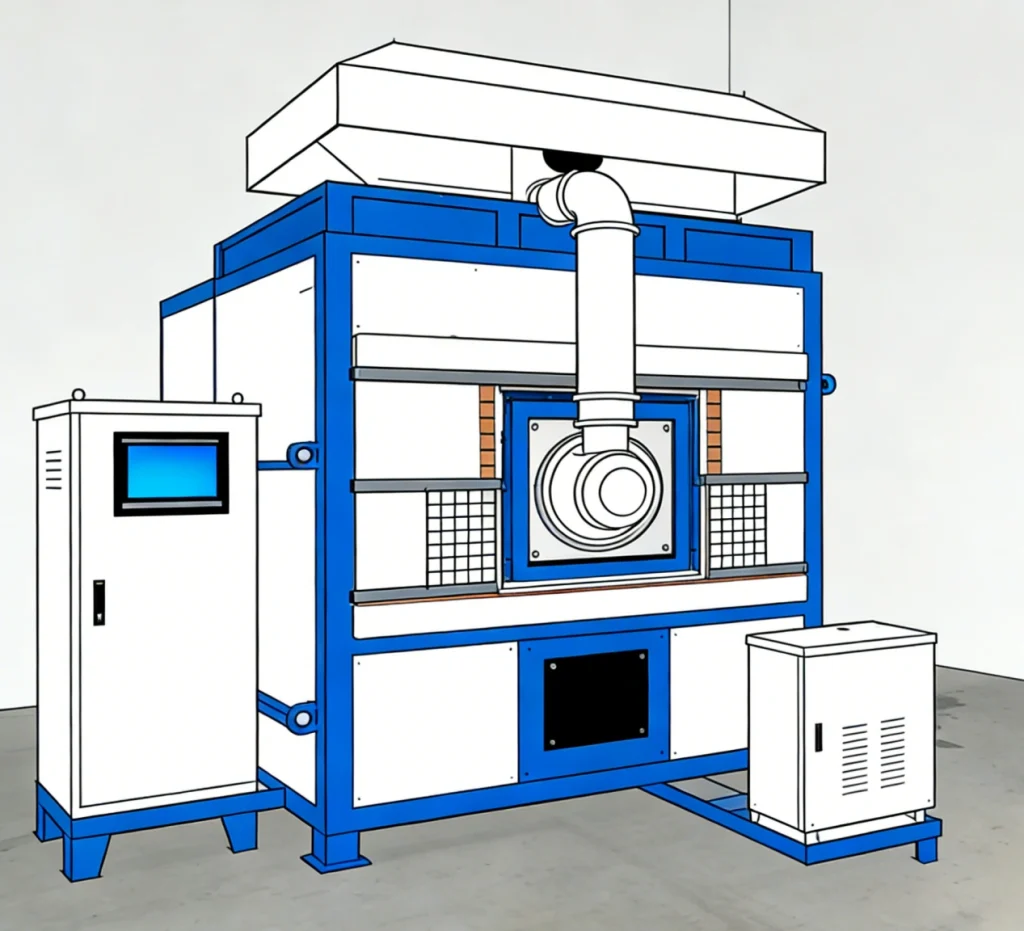
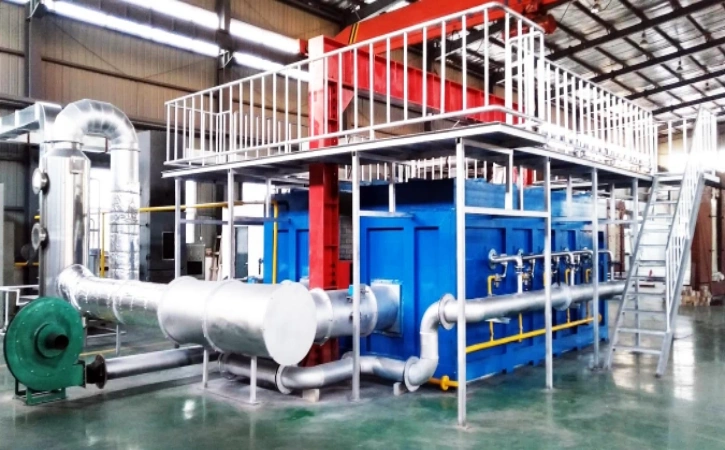
Detailed Information

【Testing Items】The vertical comprehensive fire resistance testing furnace is used to test the fire resistance limit time for the loss of integrity and thermal insulation of specimens such as fire doors, fire windows, fire partitions, fire-resistant glass, and fire shutters.
【Applicable Standards】
GB 9978 “Fire Resistance Test Methods for Building Components,”
GB/T 38252 “Test Method for Fire Integrity of Building Doors and Windows”
【Technical Parameters】
- Furnace internal dimensions: 3.0m × 3.0m × 1.2m (customizable for 5.0m × 5.0m × 1.2m and larger sizes)
- Fuel: Liquefied petroleum gas or natural gas
- Maximum operating temperature: 1300°C
- Number of burners: 6 sets
- Exhaust gas temperature: <100°C
- Exhaust gas flow rate: Approximately 10000 m³/h
- Furnace wall temperature rise: < ambient temperature +40°C (excluding areas around burners and observation windows)
- Insulation material: Internal lining with zirconia-containing fiber modules.
- Observation windows: 4 on the rear wall of the furnace
- Thermocouples: 9 furnace thermocouples; 30 back-face thermocouples, 1 movable thermocouple, 1 ambient thermocouple. Thermocouples comply with GB 9978.1 standards and are nickel-chromium/nickel-silicon (K-type) thermocouples as per GB/T 16839.1. Furnace thermocouple accuracy: ±15°C; back-face thermocouple accuracy: ±4°C; movable thermocouple accuracy: ±4°C; ambient thermocouple accuracy: ±1°C.
The back-face test is equipped with 30 interfaces, allowing simultaneous measurement of 30 back-face temperatures.

【Testing Items】Used to determine the fire resistance limit time of components such as fireproof coatings for steel structures and horizontal partitions.
【Applicable Standards】
GB/T 9978.1 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 1: General Requirements,”
GB/T 9978.3 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 3: Test Methods and Commentary on Test Data Application,”
GB/T 9978.5 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 5: Specific Requirements for Loadbearing Horizontal Separating Elements,”
GB/T 9978.6 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 6: Specific Requirements for Beams,”
GB/T 9978.9 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 9: Specific Requirements for Non-Loadbearing Ceiling Elements”
【Technical Parameters】
- Furnace internal dimensions: 4.2m × 3.0m × 1.5m
- Fuel: Liquefied petroleum gas or natural gas
- Maximum operating temperature: 1300°C
- Number of burners: 10
- Specimen installation method: External mounting
- Exhaust method: Mechanical exhaust at the rear
- Combustion control method: Proportional combustion, automatic furnace pressure control, automatic temperature adjustment, programmed temperature curve control, computer-assisted management
- Operating voltage: AC 380V ±10%, 50Hz, 70kW
- Test temperature: Complies with the test temperature curve specified in relevant standards.
- Microcomputer control, computer operation;
- Exhaust gas treatment system capacity: >11000 m³/h, temperature resistance ≥400°C
- Air supply volume: >3200 m³/h
- Remote real-time monitoring, data transmission, and automatic equipment detection
- Beam test loading self-reaction frame: Load capacity 400 kN, maximum deformation ≤0.5 mm, four-point synchronous loading, servo hydraulic loading type.
- Equipment installation space: Length × Width × Height (mm): 11000 × 14000 × 5500.

【Testing Items】Tests the fire resistance limit performance of various ventilation duct components.
【Applicable Standards】
GB/T 9978.1 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 1: General Requirements,”
GB/T 17428 “Fire Resistance Test Method for Ventilation Ducts”
【Technical Parameters】
- Furnace temperature: Complies with the standard time-temperature curve specified in GB/T 9978.1
- Furnace internal dimensions: 4.5m × 4.0m × 2.0m
- Fuel: Liquefied petroleum gas or natural gas
- Maximum operating temperature: 1300°C
- Number of high-speed burners: 16
- Specimen installation method: External mounting
- Exhaust method: Exhaust through high-temperature exhaust fan at the rear
- Combustion control method: Proportional combustion, automatic furnace pressure control, automatic temperature adjustment, programmed temperature curve control, computer-assisted management
- Self-weight: Approximately 20 tons.
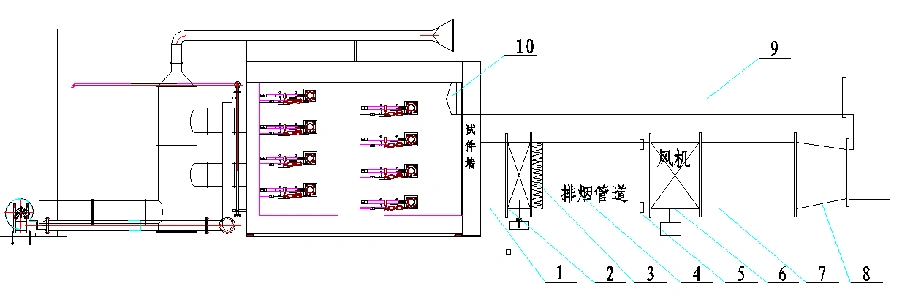
【Testing Items】Tests the fire resistance limit performance of various fireproof fan components.
【Applicable Standards】GB/T 9978.1, GA 211
【Technical Parameters】
- Furnace temperature: Complies with the standard time-temperature curve specified in GB/T 9978.1-2008
- Furnace internal dimensions: 3.0m × 3.0m × 4.5m
- Fuel: Liquefied petroleum gas or natural gas
- Maximum operating temperature: 1300°C
- Number of high-speed burners: 18
- Specimen installation method: External mounting
- Exhaust method: Exhaust through high-temperature exhaust fan at the rear
- Combustion control method: Proportional combustion, automatic furnace pressure control, automatic temperature adjustment, programmed temperature curve control, computer-assisted management
- Self-weight: Approximately 25 tons.
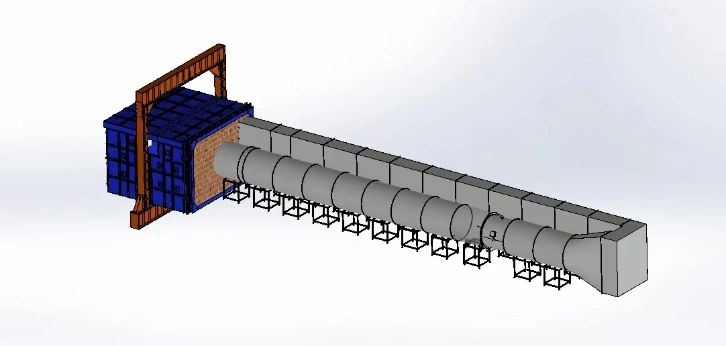
【Testing Items】Fire resistance testing for various vertical and horizontal loadbearing and non-loadbearing separating elements; fire-resistant cable trays and supports; firefighting fans; building ventilation ducts; and building components with optional and additional test procedures.
【Applicable Standards】
GB/T 9978.1 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 1: General Requirements,”
GB/T 9978.8 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 8: Specific Requirements for Non-Loadbearing Vertical Separating Elements,”
ISO 834-1 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 1: General Requirements,”
ISO 834-8 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 8: Specific Requirements for Non-Loadbearing Vertical Separating Elements,”
GB/T 17428 “Fire Resistance Test Method for Building Pipes,”
T/CECS 886 “Standard for Test Method of Fire Performance of Smoke Control and Exhaust Ducts in Buildings,”
GB/T 29415 “Test for Fire-Resistant Cable Trays,”
XF/T 537 “Test Methods for Flame Retardant, Fire Resistant, and Fireproof Performance of Busbar Trunking Systems (Busways),”
JB/T 10216 “Cable Trays for Electrical Control and Distribution,”
GB/T 9978.5 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 5: Specific Requirements for Loadbearing Horizontal Separating Elements,”
GB/T 9978.6 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 6: Specific Requirements for Beams (Horizontal Furnace),”
GB/T 9978.9 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 8: Specific Requirements for Non-Loadbearing Ceiling Elements,”
XF 211 (Draft for Review) “Fire Resistance Performance Test for Firefighting Fans,”
GB/T 9978.4 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 4: Specific Requirements for Loadbearing Vertical Separating Elements,”
GB/T 9978.7 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 7: Specific Requirements for Columns,”
GB/T 26784 Standard 4.1 Hydrocarbon Heating Curve,
GB/T 26784 Standard 4.2 Outdoor Fire Temperature Rise Curve,
GB/T 26784 Standard 4.3 Slow Heating Curve,
GB/T 26784 Standard 4.4 Electrical Fire Heating Curve,
GB/T 26784 Standard 4.5 Tunnel Fire RABT-ZTV
GA/T 714 Standard 3.7 Petrochemical Fire Test Heating Curve;
【Technical Parameters】
- Furnace internal clear dimensions: 4500mm (D) × 4500mm (W) × 3000mm (H).
- Fuel: Liquefied petroleum gas/natural gas.
- Number of integrated burners: Not less than 30.
- Core components of the combustion system use well-known brands, such as solenoid valves, proportional valves, pressure reducing valves, actuators, pressure switches, flame detection probes, combustion controllers, etc.
- Ventilation duct system: Two sets to meet simultaneous testing requirements for Duct A and Duct B.
- Cable tray testing system (including control cabinet, single-phase transformer, three-phase star-connected transformer, electrical components, fire-resistant supports, etc.).
- Beam test loading self-reaction frame: Load capacity 400 kN, maximum deformation ≤0.5 mm, four-point synchronous loading, servo hydraulic loading type.
- Firefighting fan duct: Accommodates axial flow (and corresponding centrifugal) fire exhaust fans with model number ≤ NO18 for high-temperature testing in the laboratory. Ducts are standardized (refer to GB/T 1236-2000).
- Column test loading self-reaction frame: Load capacity 1000 kN, maximum deformation ≤0.5 mm, single-point concentrated load, servo hydraulic loading type.
- Operating voltage: AC 380V ±10%, 50Hz; Power consumption: 100 kW.

【Testing Items】Fire performance testing for building curtain walls.
【Applicable Standards】
GB/T 41336 Classification and Test Method for Fire Performance of Building Curtain Walls
【Technical Parameters】
- Furnace internal dimensions: 10m × 6m × 2m
- Fuel: Liquefied petroleum gas/natural gas
- Maximum operating temperature: 1300°C
- Number of burners: 40
- Specimen installation method: External mounting
- Exhaust method: Mechanical exhaust at the rear
- Combustion control method: Proportional combustion, automatic furnace pressure control, automatic temperature adjustment, programmed temperature curve control, computer-assisted management
- Operating voltage: AC 380V ±10%, 50Hz, 120kW
- Test temperature: Complies with the test temperature curve specified in relevant standards
- Microcomputer control, computer operation
- Monitoring camera system: 5 megapixels (optional)
- Exhaust gas treatment system capacity: >22000 m³/h, temperature resistance ≥400°C
- Remote real-time monitoring, data transmission, and automatic equipment detection
- Equipment installation space: Length × Width × Height (mm): 18000 × 16000 × 8500.

【Testing Items】When conducting fire resistance tests on building separating elements according to the test methods specified in GB/T 9978.1, a water spray impact test can be additionally performed as needed.
【Applicable Standards】
GB 9978.1 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components”
GB/T 26784 “Optional and Additional Test Procedures for Fire Resistance Tests of Building Components”.
JSW-FHM-CYL Fire Door Total Smoke Production Tester
【Testing Items】Overall smoke production characteristic test for fire doors.
【Applicable Standards】
GB/T 9978.1 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 1: General Requirements,” GB/T 9978.3 “Fire Resistance Tests for Building Components – Part 3: Test Methods and Application of Test Data,”
GB/T 12955 “Fire Doors”

【Testing Items】Used for purification of combustion exhaust gases.
【Applicable Standards】
“Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China” and other relevant environmental protection laws, regulations, and rules;
“Regulations on the Administration of Environmental Protection for Construction Projects,” State Council Decree [1998] No. 253;
“Decision on Several Issues Concerning Environmental Protection,” State Council Document [1996] No. 31;
GB 50160 “Code for Fire Protection Design of Petroleum and Chemical Enterprises”;
Secondary standard in GB 13271 “Emission Standard of Air Pollutants for Boilers”;
Secondary standard in GB 16297 “Integrated Emission Standard of Air Pollutants”;
JGJ 141 “Technical Specification for Ventilation Ducts”;
GB 12348 “Noise Limits for Industrial Enterprises at Boundary”
“Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Waste”

【Testing Items】Used to test the smoke containment performance of fire doors.
【Applicable Standards】
GB/T 41480 “Test Method for Smoke Containment Performance of Doors and Shutters”
【Technical Parameters】
- Maximum test specimen size: 3m × 4m;
- Hot air circulation method: 4 circulation fans, single unit power 1.5 kW;
- Pressure measurement and control range: Range -100 to 100 Pa, accuracy ±1%, total of two units;
- Flow measurement and control range: DN32 range 2–70 Nm³/h, accuracy ±1.5%; DN50 range 10–250 Nm³/h, accuracy ±1.5%;
- Temperature measurement range: 0–250°C, total of 12 measurement points, error < ±5°C;
- Test temperatures: Ambient 20±10°C, medium temperature 200±20°C;
- Heating method: Heating tubes 380V, single tube 4 kW, total 96 kW;
- Specimen frame: Made of profiles + steel plates, high-temperature resistant sealant seals joints between plates and profiles. Provides one set of 2.1m×2.4m opening, one set of 2.4m×2.7m opening specimen frames, total three sets (other opening size specimen frames can be customized);
- Equipment furnace body footprint (L×W×H): 4.5m × 3.5m × 5m;
- Equipment specimen frame base footprint (L×W): 2.6m × 3.6m;
- Equipment power supply: 380V, 120 kW.
Fire resistance test furnaces are the key equipment used to measure how well building materials and products can stand up to fire. They work by simulating a controlled fire environment and measuring different failure points. The primary function of the equipment is to apply precise thermal loads according to international and national time-temperature curves, enabling the verification of a specimen’s ability to maintain structural integrity (E), insulation (I), and load-bearing capacity (R) over a required duration. These systems facilitate the identification of failure modes and ensure compliance with stringent fire safety regulations.
Thermal Performance
Maximum operating temperature up to 1300°C, capable of following standard, hydrocarbon, external fire, and other specialized time-temperature curves.
Loading Systems
Integrated servo-hydraulic loading frames for structural tests to simulate mechanical loads during fire exposure.
Ancillary Systems
Comprehensive solutions including water spray impact test apparatus, total smoke production and smoke leakage measurement systems, and high-capacity fume purification units for exhaust gas treatment.
Control & Measurement:
Fully automated control of temperature, pressure, and combustion. Advanced data acquisition for furnace temperature, specimen back-face temperature, displacement, and pressure differentials.
Creating a Controlled Fire
▪The furnace uses an array of gas burners to create a uniform fire inside a sealed chamber
▪A computerized control system carefully follows standard time-temperature curves
▪The system controls air flow and pressure to make sure heat spreads evenly
Measuring When Products Fail
▪Integrity failure: Detects when flames break through using special cotton pads or gauges
▪Insulation failure: Measures temperature rise on the “cold side” using multiple thermocouples
▪Load-bearing failure: Uses hydraulic systems to add weight while monitoring how much the product bends or deforms
Special Testing Capabilities
▪Water spray systems to simulate firefighting conditions
▪Smoke measurement systems
▪Pressure control to simulate wind conditions during fires
Development History of Fire Resistance Test Furnaces
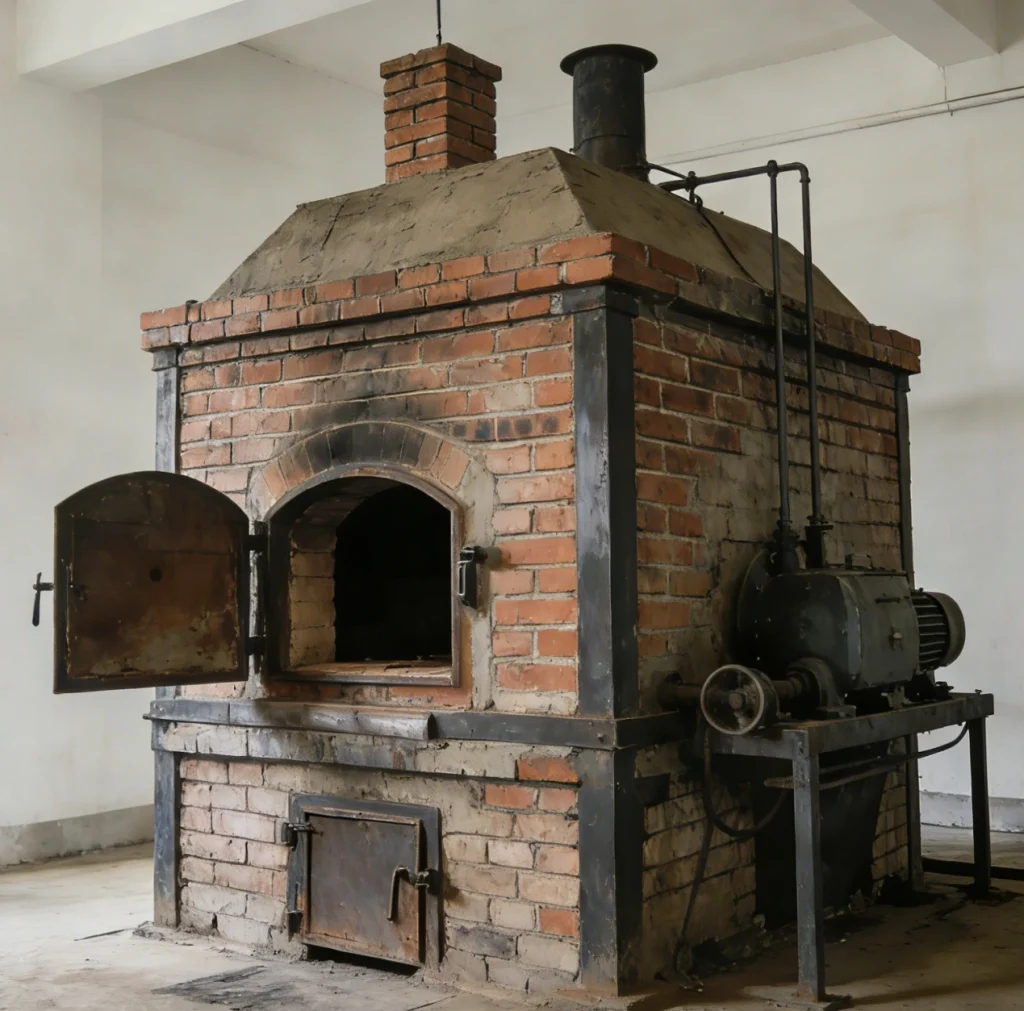

Basic Furnaces(1950s-1970s)
▪Used coal or oil for heating (poor temperature control)
▪Manual recording of test results
▪Could only test simple wall sections
▪Example: Early brick furnaces
Standardization Era(1980s-1990s)
▪Switched to gas heating (better temperature control)
▪Added multiple temperature sensors and simple loading systems
▪Could perform tests according to new national standards
▪Used separate control panels with analog recorders
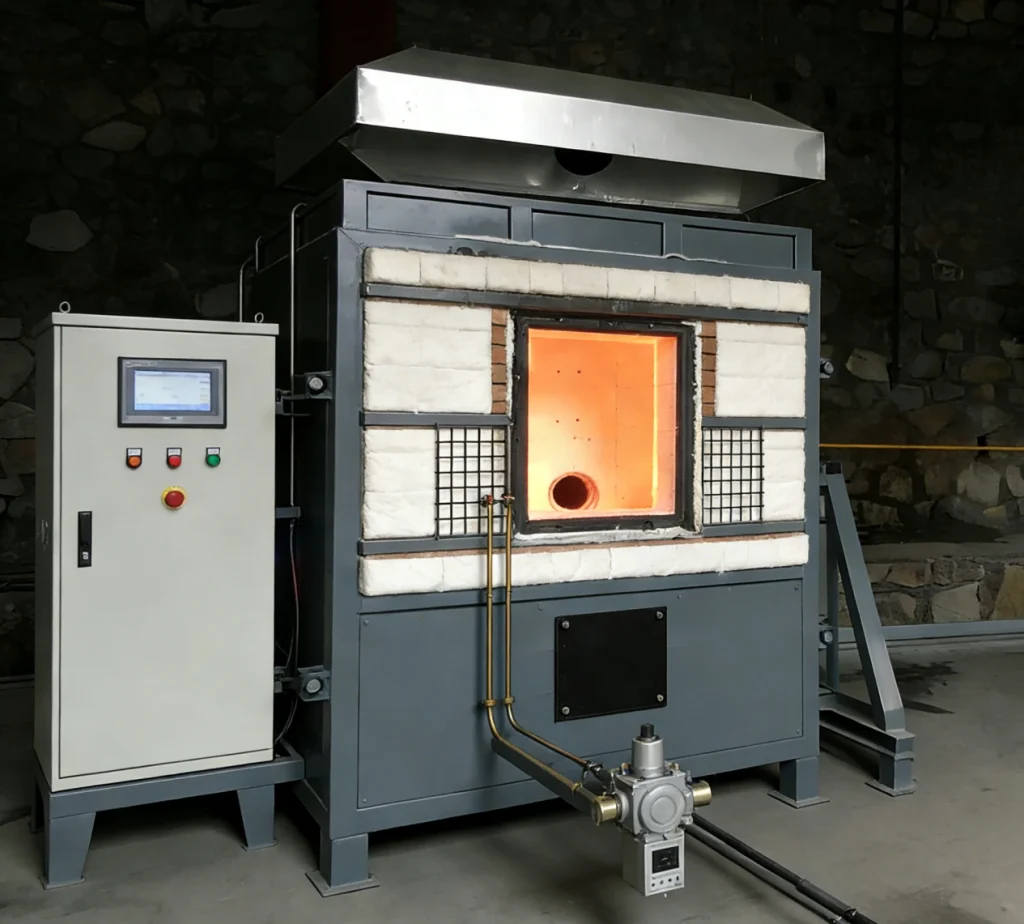


Automation Era(2000s-2010s)
▪Fully automatic computer-controlled burners
▪Digital data collection systems
▪Specialized furnaces for different test types
▪Added basic video monitoring and smoke cleaning
Smart Systems(2010s-Present)
▪Can switch between different fire curve types automatically
▪Real-time 3D temperature monitoring
▪Integrated loading and measurement systems
▪Remote monitoring capabilities
▪Environmentally friendly smoke cleaning systems
▪Example: Modern comprehensive test furnaces with 30+ burner control points
Technical Progress:
▪Control accuracy: Improved from ±50°C to ±5°C (furnace temperature)
▪Data collection: From single temperature to multiple measurements
▪Standards: Now meets international testing requirements
▪Energy efficiency: Burner efficiency improved from 40% to over 85%
▪Safety: From manual to fully automated safety systems
▪Current Advanced Technology:
▪Digital twin systems for test simulation
▪Multi-hazard testing (fire + earthquake + wind)
▪Linking heat patterns to material changes
▪Developing cleaner fuel systems
Fire test furnaces have evolved from simple heaters to complex scientific systems that combine combustion technology, precision measurement, automation, and materials science. They are essential equipment for building safety worldwide.