High-end Bearing Testing Machine
Home>>Testing Rig>>Aerospace System
Aerospace System
SINOTEST is committed to effectively solve the testing machine required for bearing development testing. It has helped to further improve and enhance the process testing methods, product inspection and testing methods, and comprehensive performance testing methods of related bearing products. It enhances the research and development capabilities, independent innovation capabilities, and core competitiveness of high-end bearings.
AVAILABLE MODELS
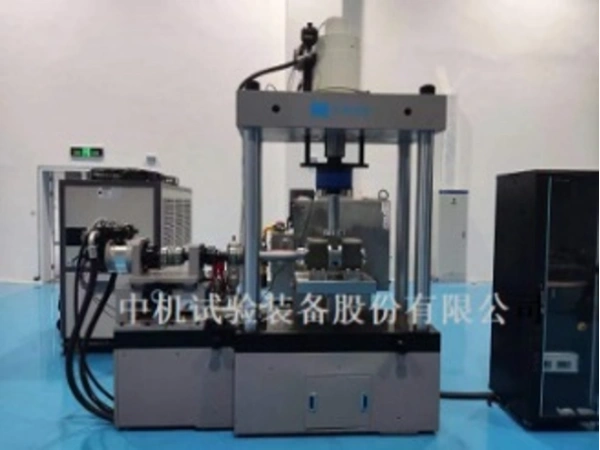

Dual axis alternating load joint bearing testing machine
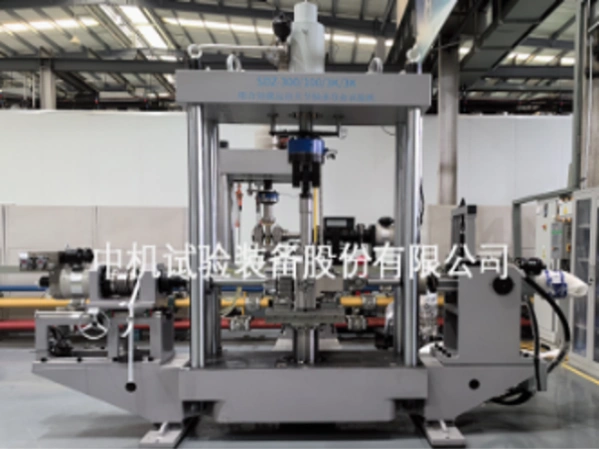

Four axis alternating load joint bearing testing machine

Ball joint bearing testing machine
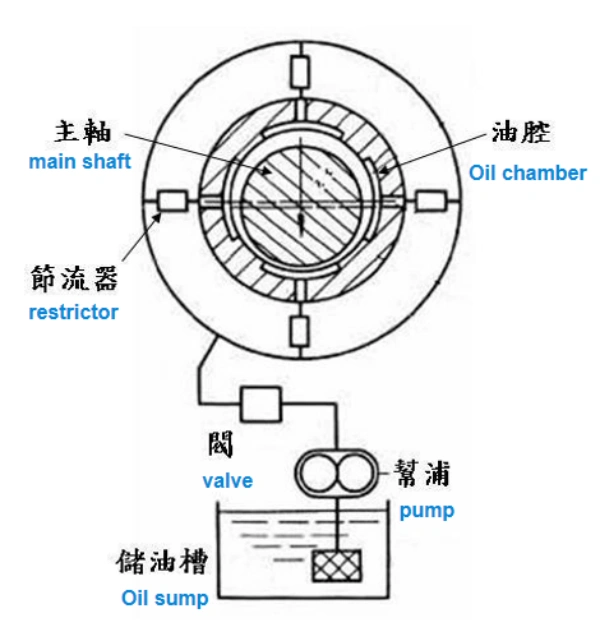
Static pressure support technology
Hydraulic static pressure bearings are sliding bearings that operate under liquid static lubrication. Usually, it relies on an external oil supply system to supply pressure oil to the bearings, which is conveyed to the oil chamber of the bearings through compensation elements, forming a lubricating oil film with sufficient pressure to float the shaft diameter. The external load is supported by the static pressure of the liquid, ensuring that the shaft diameter is in a state of complete liquid friction with the bearings at any speed (including zero speed) and predetermined load. The commonly used constant pressure oil supply hydrostatic bearing system consists of three parts: radial and thrust bearings, compensation components, and oil supply devices;
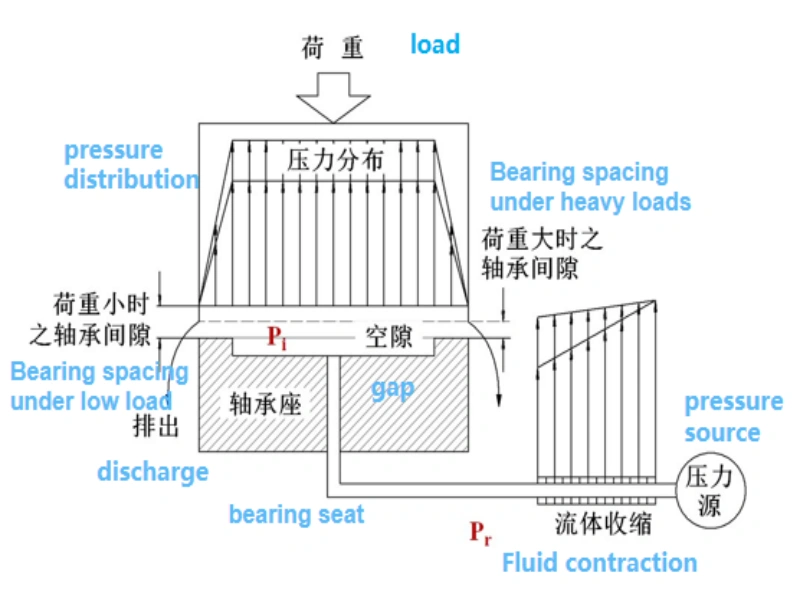
Static pressure support technology
When the oil chamber is filled with hydraulic oil, the bearing platform will float, and the initial clearance h0 of the stroke is separated by one side of the oil film between the bearing platform and the bearing base. When the bearing platform receives an external load (load) W, it will reduce the oil film gap to h (<h0), increase the resistance of oil return in the oil chamber, and increase the pressure in the oil chamber to Pi (Pi>Pr) to resist the external load W and maintain the bearing platform in a balanced state in hand, allowing the bearing to work in a liquid friction state;